Please select your area of interest
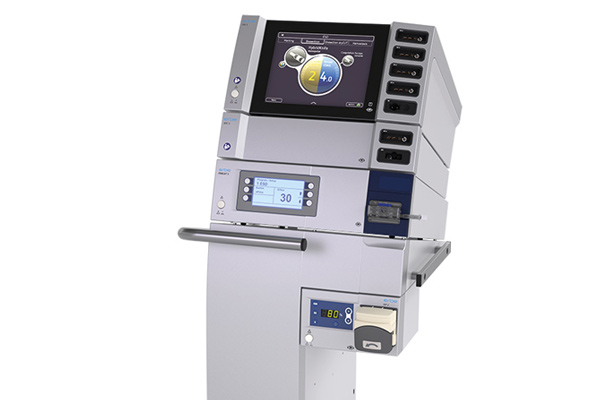
Workstation
This combination of units and instruments can do much more than hybrid technology.
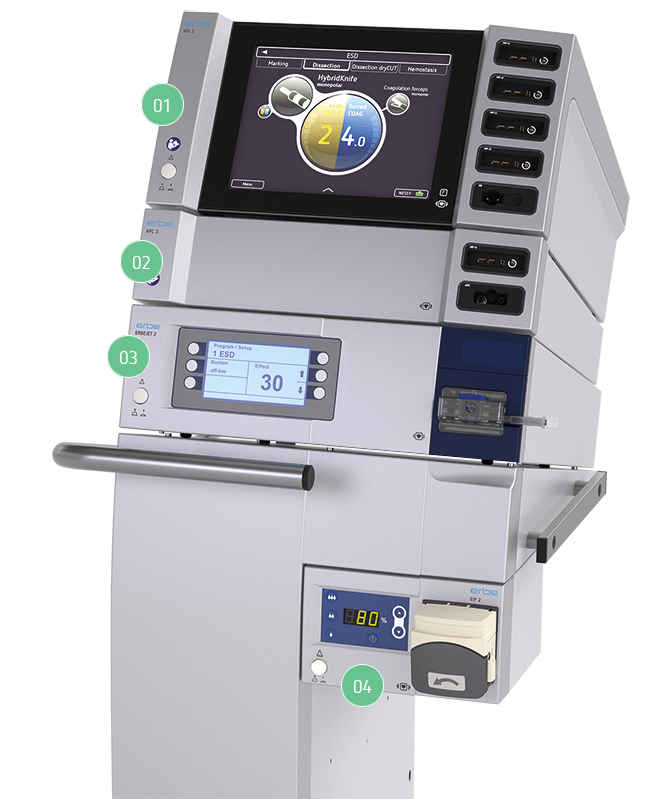





Gastroenterology workstation:

Electrosurgical unit VIO 3

APC 3 for argon plasma coagulation

Hydrosurgery unit ERBEJET 2

Endoscopic irrigation pump EIP 2
Instruments for hybrid techniques and waterjet elevation:

HybridKnife, T-Type, I-Jet

HybridKnife, I-Type, I-Jet

HybridKnife, O-Type, I-Jet

HybridAPC

Flexible probe


We train you, accompany workshops and organise trade fairs and congresses.
Browse our training program for GI
Publications
Large case numbers, documented in numerous publications exhibit the advantages of the application solutions for clinicians and patients.
Endoscopic submucosal dissection
ESD
Conclusion of the authors: ESD of gastric neoplasias using the HybridKnife is effective and safe, faster and easier than in comparison with conventional ESD.
Link to study
Peroral endoscopic myotomy
POEM
Conclusion of the authors: POEM is considered a safe and effective treatment option for achalasia, however prospective multicenter studies are deemed necessary in order to demonstrate clinical efficiency.
Link to study
Ablation of
Barrett's Esophagus
Conclusion of the authors: The safety and effectiveness of the HybridAPC was investigated on 50 patients with Barrett's Esophagus. In addition, a transparent cap was also used as an attachment on the endoscope. HybridAPC was shown to be effective and safe in the treatment of Barrett's Esophagus. The stricture formation rate was only 2%.
Link to study
Repici A, Hassan C, Pagano N, Rando G, Romeo F, Spaggiari P, Roncalli M,Ferrara E, Malesci A.
Link to study
Repici, A et al.
Link to study
Horst Neuhaus, Rupert Mayershofer, Katja Wirths, Brigitte Schumacher, Alexander Seelhoff, Michael Vieth, Markus D. Enderle
Link to study
Cai MY, Zhou PH, Yao LQ, Xu MD, Zhong YS, Li QL, Chen WF, Hu JW, Cui Z, Zhu BQ
Link to study
Sturm C, Eickhoff A, Manner H.
Link to study
Manner H, Neugebauer A, Scharpf M, Braun K, May A, Ell C, Fend F, Enderle M.
Link to study
Downloads
Download our marketing material about hybrid technology.
Anatomy explained simply
The digestive tract viewed from the inside and in cross-section.
Removal of a tissue abnormality such as an intestinal polyp
All sections of the digestive tract - the esophagus, the stomach and the intestines - consist of 3 principal skin layers. In medical terms these are referred to as the mucosa, submucosa and muscularis.
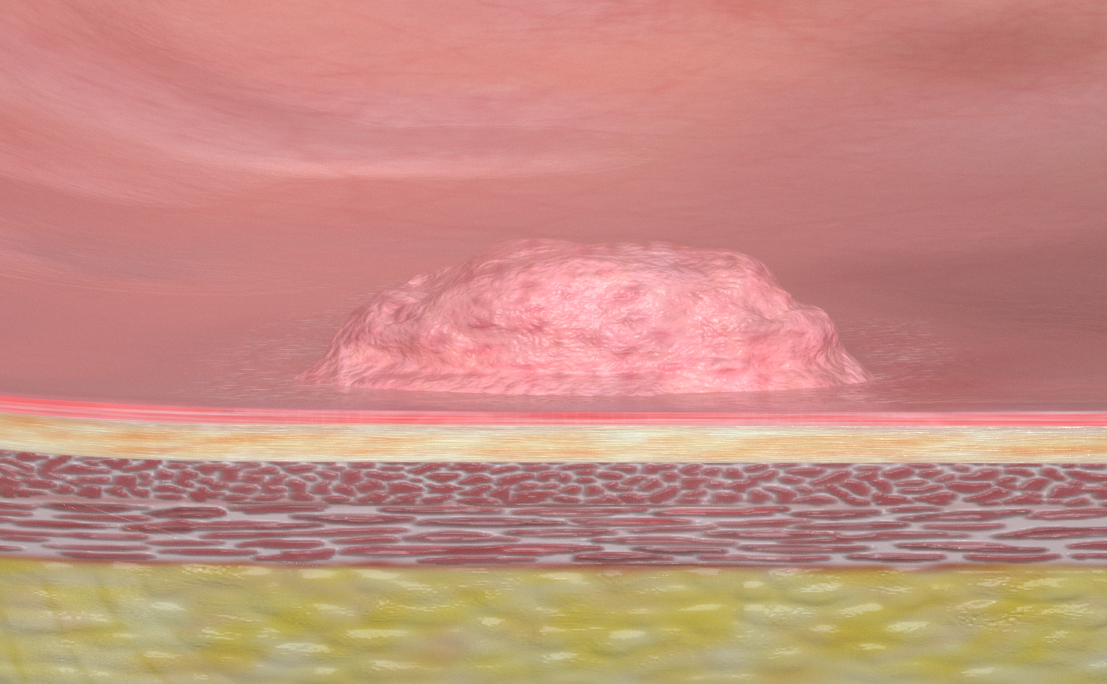
In most cases, tissue changes occur on the mucous membrane of the organ. This is the innermost layer of the intestine, for example, which comes into contact with excretion and is therefore most susceptible to changes. Polyps most frequently develop in the intestine, and although they are rarely malignant, they still have to be removed. Under oncologic principles this should be done completely and in one piece (en bloc), only then can it be safely proven that no cells of the altered tissue have remained in the healthy tissue.
A major advantage for the patient: minimally invasive endoscopic resection often saves the need for surgery.
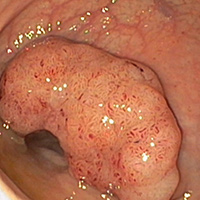
Image of a small pedunculated polyp. This polyp can be removed with a snare cut in one piece.
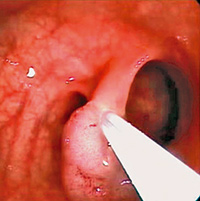
Image of a larger, broad-based polyp. This polyp cannot be removed in one piece without special instruments and techniques, but must be fragmented.
Tissue changes in the esophagus
The mucous membrane as the innermost layer of the esophagus can change due to various influences. A frequent cause may be gastric acid, which flows back into the esophagus as reflux and attacks and alters the structure of the mucous membrane. The clinical picture of this first phase is referred to as Barrett's Esophagus and can be reversed by thermal exposure. Further phases of mucous membrane changes can also be treated therapeutically, for example by electrosurgically ablating the layer.
Dysphagia in the esophagus
Patients with difficulties in swallowing (achalasia) may have a dysfunction of the esophageal muscles. This outermost layer of the esophagus has the function of transporting the chyme into the stomach through peristalsis. If the function of the esophageal sphincter is diminished and there is no or diminished relaxation of the esophageal sphincter in the stomach, a muscular constriction develops in this section of the esophagus. This constriction can be widened by splitting of the ring muscles (myotomy).
Medical advantages of the procedures
As a patient you benefit in several ways.
- Faster and easier as fewer instrument changes are required
- Large polyps of the rectum can be treated and healed reliably and effectively in one piece
- 85% of these polyps can be removed in one piece
- In about 90% of patients, gastric tumors can be cured completely
- Therefore, leading internists are of the opinion that the procedure can establish itself as the method of choice
- Often the esophagus can be preserved
- As a result, the functionality of the organ and the quality of life of the patient are also preserved
- Lower rate of complications
- Shorter procedure and anesthesia. Hospitalization is also reduced
Questions and answers
Answers for the most important questions.
The physician examines the inside of your body via a flexible optical instrument, a so-called endoscope. The physician can, for example, not only localize and recognize changes in the mucous membrane, but also treat them immediately.
As endoscopy can be unpleasant and painful, you will first be given a sedative and painkiller. Removal of the polyp, a polypectomy, is in itself generally painless.
You should not eat for at least 6 hours nor drink for 2 hours before the procedure.
The intestines must be cleaned thoroughly. Therefore, please follow the instructions for eating, drinking and bowel cleansing given by your doctor exactly. Avoid foods rich in fibers and containing seeds for a few days before the procedure, such as wholemeal bread, grapes, etc., which have a longer dwell time in the intestines.
Despite the utmost care of the endoscopy team, complications may occasionally occur during these procedures. During your medical consultation, your physician will inform you about possible risks.
You will feel tired for some time after the procedure; during this time you will be cared for and monitored until all organ functions are stable. Gastric surgery can result in nausea, irritation of the throat and difficulty in swallowing, or a blocked nose. Air remaining in the stomach and duodenum can cause short-term pain. In a polypectomy, painful flatulence due to air remaining in the intestines is possible. After anesthesia of the throat, short anesthetics or sedation, you must not eat or drink for at least 1 hour. And you must not actively participate in road traffic for 24 hours, not even as a pedestrian. The best thing to do is have an adult pick you up and take care of you at home for the first 24 hours. Dangerous work is taboo during this time, as are alcohol and nicotine. You should inform your attending physician or family doctor immediately if blood leaks from the anus or in case of pain, dizziness, fever or vomiting of blood.
This is not an official information sheet and does not replace a preparatory discussion with your hospital. Please consult your attending physician for more information. The content is based on the information sheets "Documented Patient Information", published by proCompliance in Thieme Compliance GmbH, Am Weichselgarten 30, 91058 Erlangen, www.thieme-compliance.de
A polyp is a mostly benign growth of the mucous membrane that can develop in the esophagus, stomach or intestines. Polyps must be removed as early as possible and examined for malignancy.
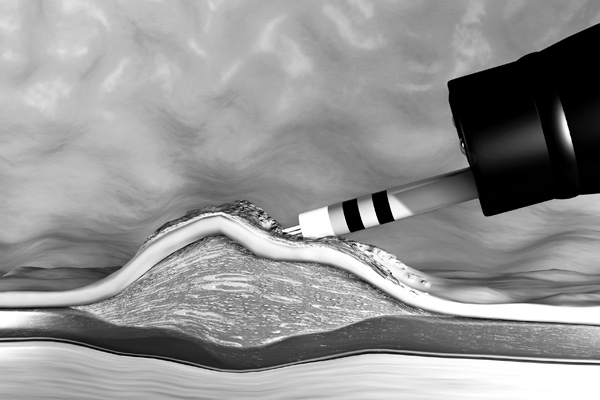
Polyps can be mushroom-shaped with a stalk, or moss-shaped flat. The former can be grasped with an electric snare, separated near the base and retrieved via the endoscope. As with a gastroscopy or colonoscopy, abdominal surgery is generally not required. Larger flat polyps that cannot be removed with a single snare size are somewhat more demanding to treat, but can also be treated endoscopically. Before being removed, a liquid, possibly with an added dye, should be injected under this type of polyp. This elevates the mucous membrane including the polyp and allows it to be separated as a whole with an electrosurgical snare or a knife electrode. Depending on the polyp or medical condition, the physician will choose the optimal treatment concept for you.
In cooperation with leading physicians, we have developed a new hybrid technology: The affected area is first marked with coagulation points, the polyp is injected and removed, bleeding is stopped at the end of the procedure, all with the same instrument. At an international level, many physicians are convinced of this technique and regard it as possible future method of choice.
As the distance to the outer organ layer is increased by the fluid cushion, it remains protected during the entire procedure - even against thermal injury*. The reason being that cutting is done with electricity, i.e. with heat.
This is not an official information sheet and does not replace a preparatory discussion with your hospital. Please consult your attending physician for more information. The content is based on the information sheets "Documented Patient Information", published by proCompliance in Thieme Compliance GmbH, Am Weichselgarten 30, 91058 Erlangen, www.thieme-compliance.de
A possible reason for the complaints when swallowing chyme can be a lack of muscle relaxation of the lower section of the esophagus. In other words, the esophagus tries to press against the high resistance in the lower sphincter muscle at the stomach entrance and narrows the section. At a later stage, the muscular tube becomes increasingly limp and loses its peristaltic function, which transports the chyme into the stomach. Both stages, first the narrowness and the later slackening of the muscle, are responsible for the complaints.
Both drug therapy as well as Botox injection or balloon dilatation (pneumatic dilatation) are possible. However, the most effective therapy providing long-term treatment success is a separation of the lower esophageal muscles, called a myotomy. This procedure can be performed laparoscopically or endoscopically.
In laparoscopic Heller myotomy, the existing standard technique, small incisions are made to access the abdominal wall. This surgical procedure is therefore performed from the outside. The new endoscopic technique POEM (Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy) does not require incisions in the abdominal cavity. The cutting instrument is inserted inside the esophagus via an endoscope, making the technique less invasive.
The muscle tissue can be myotomized precisely and flexibly, theoretically even over the entire length of the esophagus. It does not need to be exposed or mobilized during the procedure and remains attached to the connective tissue - in its natural suspended condition.
The muscle fibers are split underneath the mucous membrane. To do this, a tunnel is prepared in the submucosa between the mucous membrane and the muscle layer. The myotomy is then "covered" by the mucous membrane, which covers the separated section of the esophagus after the procedure like a plaster.
The duration of the stay depends on the individual healing process and in the case of normal progress only a few days.
This is not an official information sheet and does not replace a preparatory discussion with your hospital. Please consult your attending physician for more information. The content is based on the information sheets "Documented Patient Information", published by proCompliance in Thieme Compliance GmbH, Am Weichselgarten 30, 91058 Erlangen, www.thieme-compliance.de
The structure of the tissue in the original mucosal layer of your esophagus has changed. This transformation process takes place in stages: a Barrett's Esophagus can develop into a low-grade malformation (dysplasia). The next stages can be a severe dysplasia as a precancerous stage or even a malignant tumor, a so-called Barrett's carcinoma.
This is usually due to the frequent reflux of gastric juices (reflux) into the esophagus. Approximately 10% of patients with chronic heartburn develop a Barrett's Esophagus. Recurrent inflammations or acid burns can also be the cause.
The development risk from a Barrett's Esophagus without dysplasia to esophageal cancer is up to 0.5% per patient year, so treatment is indicated from this stage onwards. If a malignant tumor has developed over several stages, the predicted 5-year survival rate is only under 20%.
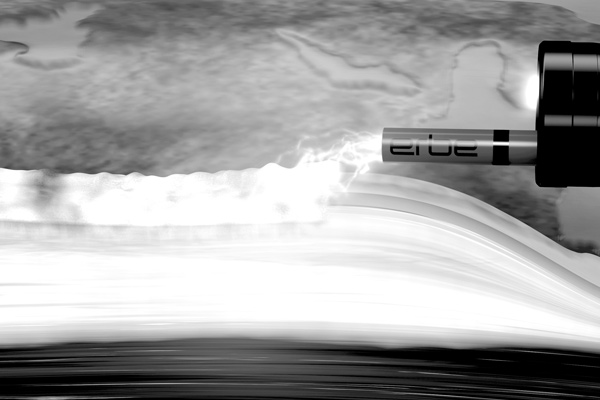
One of the therapeutic options is the ablation of the affected mucous membrane with heat. In argon plasma coagulation, electric current is transferred contact-free to the diseased tissue and kills it. The heat effect must be sufficiently large to achieve complete destruction. With this therapy, there is a risk that structures close to the wall may be thermally damaged, which can lead to a partial narrowing of the esophagus.
Before the application of heat, the mucous membrane is elevated by means of a waterjet. The thermal energy can now be applied sufficiently deep without damaging the external structures such as the muscle layer of the esophagus and causing constrictions, so-called strictures. This prevents constrictions and protects healthy adjacent tissue, while at the same time treating the affected mucous membrane even more effectively.
This is not an official information sheet and does not replace a preparatory discussion with your hospital. Please consult your attending physician for more information. The content is based on the information sheets "Documented Patient Information", published by proCompliance in Thieme Compliance GmbH, Am Weichselgarten 30, 91058 Erlangen, www.thieme-compliance.de
Important notice!
The information on this page does not replace a personal consultation with your physician. Always consult your physician in matters relating to diagnosis and treatment.